
In a subset of diplotene nuclei, a coiled organization of chromosome axes can be clearly resolved (three-dimensional volume renderings in Fig. 2) and HIM-3 (not depicted) continue to localize along the lengths of desynapsing chromosomes, but whereas REC-8 and HIM-3 signals appear as extended linear stretches in pachytene nuclei, this linear appearance gives way to a more convoluted appearance as nuclei enter diplonema. SC disassembly at the pachytene–diplotene transition is accompanied by a major transition in the organization of chromosome axes. elegans meiosis either end of a given chromosome has the potential for kinetic activity, and the position of the crossover determines which region will retain cohesion and lead the way toward the pole at meiosis I ( Albertson et al., 1997). Whereas diakinesis-stage bivalents in worms and mice are quite similar in their cytological appearance, during C. However, this strategy is inadequate to explain how two-step loss of cohesion is accomplished in organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans that do not have localized centromeres. In organisms with localized centromeres, two-step loss of cohesion is accomplished using protector proteins that localize to centromeres and shield centromeric cohesin from removal at meiosis I ( Moore et al., 1998 Kitajima et al., 2004). The connections afforded by chiasmata necessitate a two-step loss of sister chromatid cohesion: partial loss of cohesion at meiosis I permits dissolution of chiasmata and homologue separation while maintaining the connections between sisters needed to permit congression and bipolar spindle attachment at meiosis II. However, despite the central importance of chiasmata, we know very little about the processes of SC disassembly and chiasma emergence, or about how earlier events are coupled to these late prophase chromosome restructuring events.
A crossover between the DNA molecules of homologues and cohesion between sister chromatids on both sides of the crossover together underpin this late prophase connection, known as the chiasma, that persists after SC disassembly.

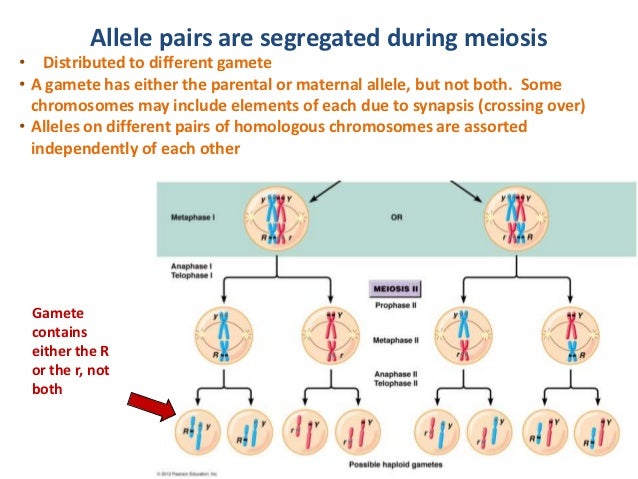
During later prophase, the SC disassembles and chromosomes undergo further structural remodeling to yield an organization in which homologues remain connected yet are oriented away from each other in a configuration that promotes their attachment to and segregation toward opposite poles of the meiosis I spindle. Chromosomes must acquire an organization that will promote both controlled DNA breakage and subsequent recombinational repair using the homologous chromosome as a repair partner to yield interhomologue crossovers this organization includes meiosis-specific differentiation of chromosome axes and loading of proteins comprising the central region of the synaptonemal complex (SC), a structure linking the axes of aligned homologues. Structural remodeling of chromosomes is an integral feature of the meiotic program by which diploid germ cells generate haploid gametes ( Page and Hawley, 2003). We propose that crossovers or crossover precursors serve as symmetry-breaking events that promote differentiation of subregions of the bivalent by triggering asymmetric disassembly of the SC. Moreover, a γ-irradiation treatment that restores crossovers in the spo-11 mutant also restores asymmetry of SYP-1 localization.
#CROSSING OVER PROPHASE 1 FULL#
This and other manifestations of asymmetry along chromosomes are lost in synapsis-proficient crossover-defective mutants, which often retain SYP-1,2 along the full lengths of coiled diplotene axes. Chromosome shortening during diplonema is accompanied by coiling of chromosome axes and highly asymmetric departure of synaptonemal complex (SC) central region proteins SYP-1 and SYP-2, which diminish over most of the length of each desynapsing bivalent while becoming concentrated on axis segments distal to the single emerging chiasma.

We have imaged remodeling of meiotic chromosome structures after pachytene exit in Caenorhabditis elegans. Homologous chromosome pairs (bivalents) undergo restructuring during meiotic prophase to convert a configuration that promotes crossover recombination into one that promotes bipolar spindle attachment and localized cohesion loss.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
